Financial applications require accurate payment card data capture without forcing users through tedious manual entry. OCR BANK-Scan provides developers with tools to extract card information from camera images in real-time, but successful implementation depends on understanding the SDK architecture and following best practices during integration.
- This guide walks through the technical process of adding bank card scanning functionality to mobile applications.
- Whether you’re building a payment platform, expense management tool, or subscription service, these implementation steps ensure reliable card data extraction while maintaining security standards and optimal user experience.

The integration process involves SDK installation, camera configuration, data extraction setup, and validation logic implementation. Developers familiar with OCR technology will recognize common patterns, though bank card scanning presents unique challenges around security, format validation, and edge case handling that require specific attention during development.
Preparation Steps Before SDK Integration Begins
Understanding your application’s specific requirements helps avoid unnecessary rework during implementation. Different use cases demand different approaches to card data handling, storage, and processing.
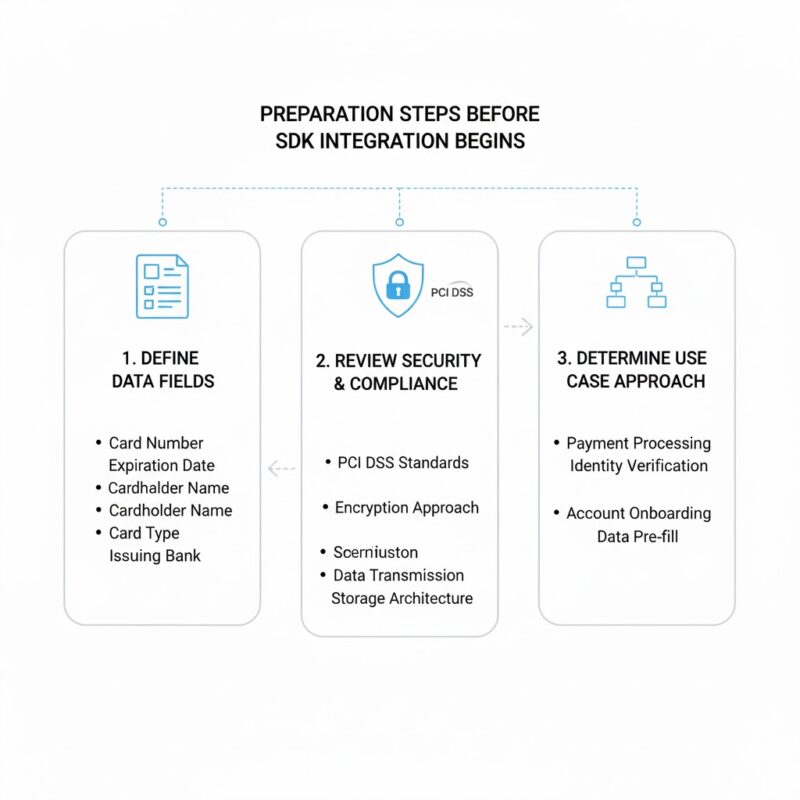
Start by defining which card data fields your application needs to extract. Basic implementations might only require card numbers and expiration dates for payment processing. More comprehensive integrations could include cardholder names, card types, and issuing bank information for verification purposes.
Review your data security requirements and compliance obligations before writing any code. Applications handling payment card information must comply with PCI DSS standards regardless of whether they store card data or pass it directly to payment processors.
This assessment determines your encryption approach, data transmission methods, and storage architecture.
Evaluate your target platforms and minimum supported OS versions. OCR BANK-Scan offers native SDKs for iOS and Android with different minimum version requirements. Cross-platform frameworks like React Native or Flutter require bridge implementations or platform-specific modules that affect your integration timeline and maintenance burden.
SDK Installation and Initial Configuration for Mobile Platforms
Installation procedures vary between iOS and Android platforms but follow similar patterns of dependency management and configuration file setup.
iOS developers using CocoaPods add the OCR BANK-Scan dependency to their Podfile and run pod install to integrate the framework. The SDK requires camera usage permissions declared in Info.plist with appropriate user-facing descriptions explaining why card scanning needs camera access. Failing to provide clear permission descriptions results in App Store rejection during review.
Android integration uses Gradle dependency management. Add the SDK repository to your project-level build.gradle file and include the OCR BANK-Scan dependency in your app-level build.gradle. The SDK requires camera permissions in AndroidManifest.xml along with appropriate runtime permission requests for Android 6.0 and higher.
Both platforms need initialization code in your application startup sequence. Create an SDK configuration object with your license key and optional settings for extraction accuracy, processing speed, and supported card types. Initialize the SDK early in your app lifecycle to avoid delays when users first access scanning functionality.
Configuration options affect extraction performance and accuracy trade-offs. High accuracy mode processes images more thoroughly but takes longer and consumes more battery. Fast mode prioritizes speed over precision, suitable for applications where users can easily rescan if extraction fails. Balanced mode provides reasonable accuracy with acceptable performance for most use cases.
Camera View Implementation and User Interface Design Considerations
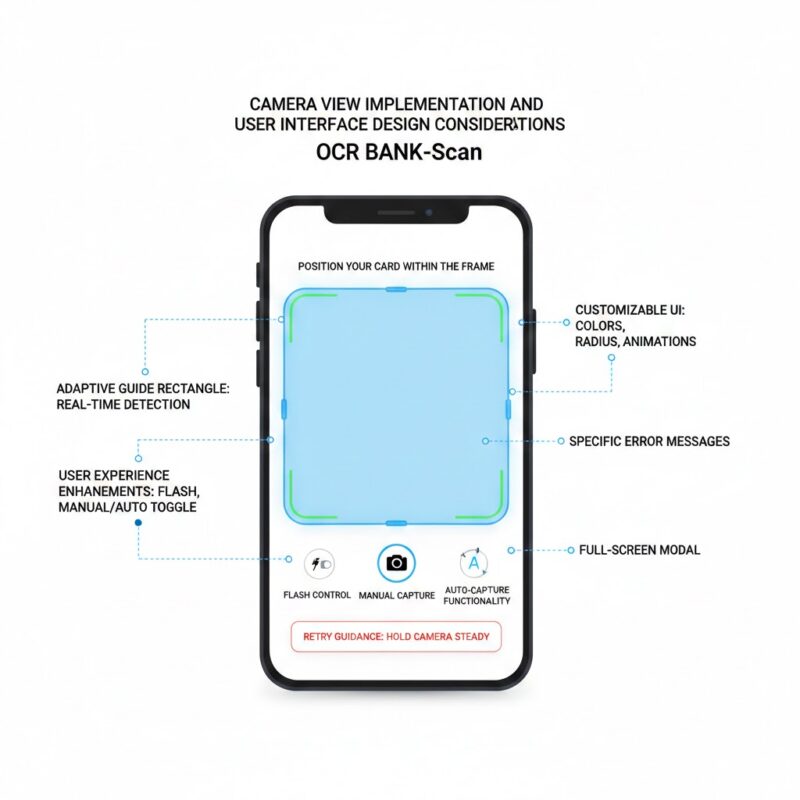
The scanning interface requires careful design to guide users toward successful card captures while providing clear feedback during the process.
OCR BANK-Scan provides pre-built camera view components that handle image capture, focus control, and real-time card detection. These components overlay guide rectangles on the camera preview showing users where to position their cards. The guide adapts to different card orientations and provides visual feedback when card edges are detected.
Developers can customize the camera interface appearance to match application branding. Adjust guide rectangle colors, corner radius, animation styles, and overlay opacity through SDK configuration parameters. Custom instruction text appears above or below the camera preview explaining what users should do.
Consider adding these user experience enhancements during camera view implementation.
- Auto-capture functionality. The SDK automatically captures images when it detects a card within the guide rectangle and determines image quality meets extraction requirements, eliminating the need for users to tap capture buttons.
- Flash control toggles. Low-light environments reduce extraction accuracy, so provide an easily accessible flash toggle that users can enable when scanning in dim conditions.
- Manual capture fallback. Some users prefer explicit control over when images are captured, so include a manual capture button alongside auto-capture functionality for those who want it.
- Retry guidance messages. When extraction fails, display specific instructions explaining why such as “Move to better lighting” or “Hold camera steady” rather than generic error messages.
The camera view typically appears as a full-screen modal or within a dedicated screen in your navigation flow. Full-screen implementations minimize distractions and help users focus on card positioning. In-flow implementations work better for applications where scanning is one step in a longer process.
Data Extraction Configuration and Field Mapping Setup
Once the camera captures card images, the SDK processes them and extracts structured data that your application can use.
Configure which data fields the SDK should extract based on your application requirements. The SDK can identify card numbers, expiration dates, cardholder names, CVV codes, and card types. Extracting only necessary fields improves processing speed and reduces battery consumption.
Data extraction returns results through callback methods or delegate protocols depending on your platform. Implement these callbacks to receive extracted card information and handle extraction failures gracefully. The callback provides a result object containing individual fields with confidence scores indicating extraction certainty.
Field mapping translates extracted data into your application’s data models.
Card numbers arrive as strings that may include spaces or dashes depending on SDK configuration.
Expiration dates come in various formats such as MM/YY, MM/YYYY, or separate month and year fields.
Your mapping logic normalizes these formats into consistent representations your application expects.
Confidence scores help determine whether extracted data requires user verification. Fields with confidence scores above 0.95 generally need no confirmation. Scores between 0.80 and 0.95 might benefit from showing users the extracted data with an option to edit if incorrect. Scores below 0.80 typically warrant prompting users to rescan or enter data manually.
Validation Rules and Error Handling for Extracted Card Data
Raw extraction output requires validation before your application uses it for payment processing or storage.
Implement Luhn algorithm validation for card numbers to catch extraction errors before sending data to payment processors. This checksum algorithm identifies transposed digits and invalid card numbers without requiring external API calls. Card numbers failing Luhn validation should trigger rescan prompts rather than proceeding to payment processing.
- Expiration date validation checks that extracted dates represent future months.
- Cards with past expiration dates are invalid and should be rejected immediately.
- Consider warning users when cards expire within 30 days, as upcoming expiration dates often indicate users need to update their payment information soon.
Card type detection through BIN analysis provides additional validation opportunities. The first six digits of card numbers identify issuing banks and card types. Validate that extracted card types match visual indicators on card images. Mismatches between detected card types and BIN analysis results suggest extraction errors requiring user confirmation.
Error handling logic determines user experience when extraction fails or produces low-confidence results. Provide specific, actionable guidance rather than generic error messages. “Card number unclear – try better lighting” helps users more than “Extraction failed – please try again.”

Consider implementing these validation and error handling patterns.
- Progressive retry strategies. After the first failed extraction, suggest minor adjustments like moving closer or holding steadier. After multiple failures, offer manual entry as an alternative to prevent user frustration.
- Partial extraction handling. When some fields extract successfully but others fail, pre-fill the successful fields and ask users to complete the missing information manually rather than discarding all extracted data.
- Format standardization. Normalize card numbers by removing spaces and dashes, standardize expiration date formats, and convert names to title case before storing or transmitting data.
- Real-time feedback during capture. Show users live feedback as the SDK detects card edges and assesses image quality, helping them adjust positioning before capture occurs.
Security Practices for Handling Sensitive Payment Card Information
Bank card data requires special security considerations throughout the extraction and handling process.
Never log complete card numbers in application logs or analytics systems. If logging is necessary for debugging, mask all but the last four digits. This practice prevents card data from appearing in crash reports, analytics dashboards, or log aggregation systems where it could be accessed by unauthorized personnel.
Encrypt extracted card data immediately after receiving it from the SDK before storing it in memory or transmitting it over networks. Use industry-standard encryption libraries provided by iOS and Android platforms rather than implementing custom encryption algorithms. For temporary storage during user sessions, use secure keychain storage on iOS or Android Keystore on Android.
Minimize the time card data remains in application memory. Process payment authorizations immediately after extraction when possible, then discard the data rather than retaining it for later use. If your application must store card data for recurring payments, use tokenization services provided by payment processors rather than storing actual card numbers.
Transmission security requires TLS 1.2 or higher for all network requests containing card data. Certificate pinning adds another security layer by ensuring your application only communicates with legitimate servers rather than potential man-in-the-middle attackers. Payment processors provide specific guidance on transmission security requirements for their platforms.
Testing Strategies and Quality Assurance for Card Scanning Features
Thorough testing ensures reliable extraction across diverse real-world conditions and card types.
Build a test card library representing various card designs, colors, and issuers. Include cards with holographic overlays, metallic finishes, and complex background patterns that challenge extraction algorithms. Test with both physical cards and high-quality printed images to evaluate performance under different conditions.
- Environment testing evaluates extraction reliability across lighting conditions, backgrounds, and camera angles.
- Test in bright sunlight, indoor fluorescent lighting, dim restaurant lighting, and complete darkness with flash enabled.
- Place cards on various background surfaces including wood tables, patterned tablecloths, and busy retail counters that might confuse edge detection algorithms.
Automated testing frameworks can validate extraction accuracy against known test cards. Create test suites that run extracted data through validation logic and compare results against expected values. These tests catch regressions when updating SDK versions or modifying extraction configurations.
Moving Forward with Bank Card Scanning Implementation
Successful OCR BANK-Scan integration balances extraction accuracy, user experience, and security requirements. Developers who carefully plan their implementation approach, thoroughly test across real-world conditions, and follow security best practices create payment experiences that users trust and prefer over manual data entry.
The investment in proper integration pays dividends through higher conversion rates, reduced user friction, and fewer support requests related to payment issues. Applications that make card data entry effortless gain competitive advantages in markets where user experience increasingly determines product success.


