As nations strive to meet ambitious net zero emissions targets, carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) technologies have emerged as pivotal solutions in the global effort to combat climate change. These technologies are increasingly recognize for their potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from hard to decarbonize sectors, thereby playing a crucial role in achieving net zero goals.
What is Carbon Capture?
Carbon capture also known as carbon capture and storage (CCS) refers to a set of technologies design to capture carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions from various sources, such as power plants and industrial facilities, before they can enter the atmosphere. The captured CO₂ is then transported, usually via pipelines and stored in underground geological formations, where it can be safely contained for centuries.
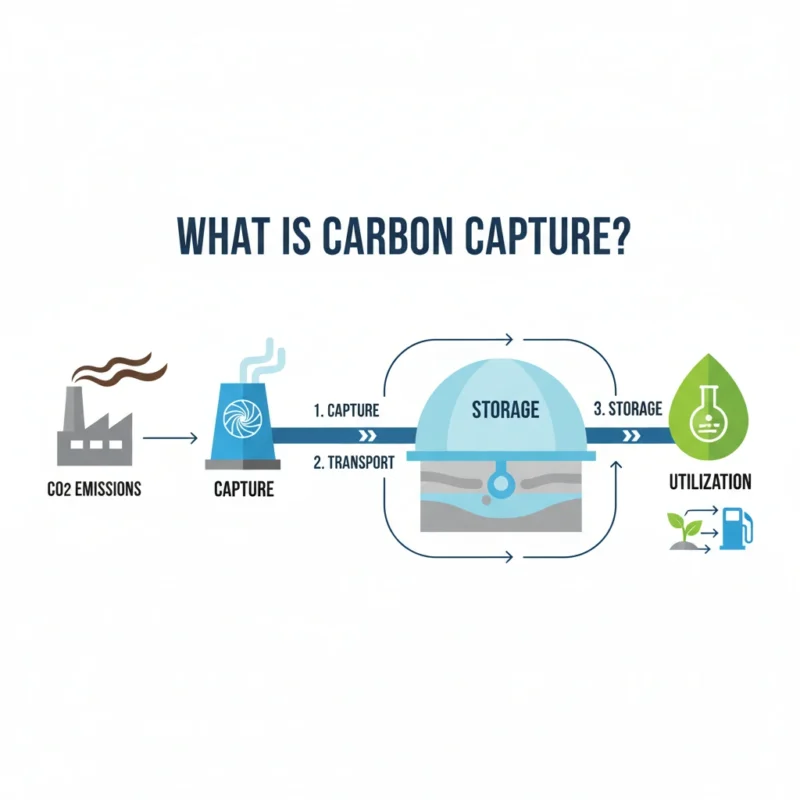
- Capture: CO₂ is separated from other gases during industrial processes or power generation.
- Transport: The CO₂ is transported to a storage site, usually via pipelines or ships.
- Storage: The CO₂ is injected deep underground, typically into depleted oil or gas fields or deep saline aquifers.
Understanding Carbon Capture Technologies
Carbon capture involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions from sources like power plants and industrial processes before they can enter the atmosphere. Once capture, CO₂ can either be store underground in geological formations, a process known as carbon storage or utilize in various applications, such as in the production of building materials or synthetic fuels. This approach not only prevents CO₂ emissions but also facilitates the development of a circular carbon economy.
The Strategic Importance of CCUS
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), CCUS technologies must account for nearly 15% of the global emissions reductions required to meet net-zero targets by 2050. This underscores the strategic importance of accelerating the deployment of CCUS to mitigate climate change effectively. However, the widespread adoption of these technologies faces challenges, including high costs and the need for supportive policies and infrastructure.
Industry Leadership
Companies like Carbon Clean are at the forefront of advancing CCUS technologies. Carbon Clean focuses on developing cost effective carbon capture solutions that enable industries to reduce their carbon footprints without compromising economic performance. Their innovative technologies aim to make carbon capture more accessible and scalable, thereby contributing to the global transition towards net zero emissions.
Policy Support and Global Initiatives
Governments worldwide are recognizing the importance of CCUS in achieving net zero targets and are implementing policies to support its development and deployment. For instance, the European Union has set a carbon injection capacity target of 50 million tonnes per year by 2030 as part of its Net Zero Industry Act. Similarly, the United States has establish an economy wide target of reducing net greenhouse gas emissions by 50 to 52% below 2005 levels by 2030, with CCUS playing a significant role in this strategy.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential benefits the deployment of CCUS technologies faces several challenges. The high costs associate with capturing and storing CO₂ remain a significant barrier. For example, direct air capture technologies, while promising, have experience slower than expect reductions in costs, with current capture costs averaging $900 per tone, far exceeding carbon credit prices and tax incentives. Additionally the scalability of these technologies and the establishment of necessary infrastructure are ongoing concerns.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|
| Role of CCUS | Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) helps reduce emissions, especially in hard to decarbonize sectors. |
| How CCUS Works | Captures CO₂ emissions from industries, stores it underground or uses it in products like fuels and building materials. |
| Global Importance | CCUS is key to achieving net zero emissions by 2050, contributing 15% of global reductions. |
| Industry Innovation | Companies like Carbon Clean are making carbon capture more affordable and scalable. |
| Government Support | Policies, such as the EU’s carbon storage target and the US emission reduction goal, support CCUS development. |
| Challenges | High costs and infrastructure needs are obstacles, with current capture costs around $900 per tonne. |
| Conclusion | CCUS is crucial for meeting national net zero targets, but requires innovation, policy and global cooperation. |
Summing It All Up
Carbon capture technologies are indispensable in the pursuit of national net zero emissions targets. While challenges such as high costs and infrastructure requirements persist the strategic importance of CCUS in reducing emissions from hard to decarbonize sectors cannot be overstate. Continue innovation, supportive policies and collaborative efforts between governments, industries and technology providers are essential to accelerate the deployment of CCUS and achieve a sustainable, net zero future.
Conclusion
Carbon capture plays an indispensable role in helping countries meet their national net zero targets. While the technology is still developing, its potential to reduce emissions from hard to decarbonize industries and create negative emissions makes it a crucial part of the global effort to combat climate change. With continued investment, innovation and collaboration, carbon capture can help secure a sustainable future for generations to come.
FAQs
- Is carbon capture the only solution to climate change?
No, carbon capture is an important tool, but it needs to be combined with efforts to reduce emissions through renewable energy, energy efficiency, and changes in consumption patterns. - How long can CO₂ be stored underground?
CO₂ can be stored underground for thousands of years if stored in appropriate geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifers. - How much does carbon capture cost?
The cost of carbon capture varies depending on the technology and scale of the project. However, costs are expected to decrease as the technology matures and economies of scale are achieved. - Can carbon capture create negative emissions?
Yes, through direct air capture, carbon capture can remove more CO₂ from the atmosphere than is emitted, helping to create negative emissions and counteract historical emissions.


